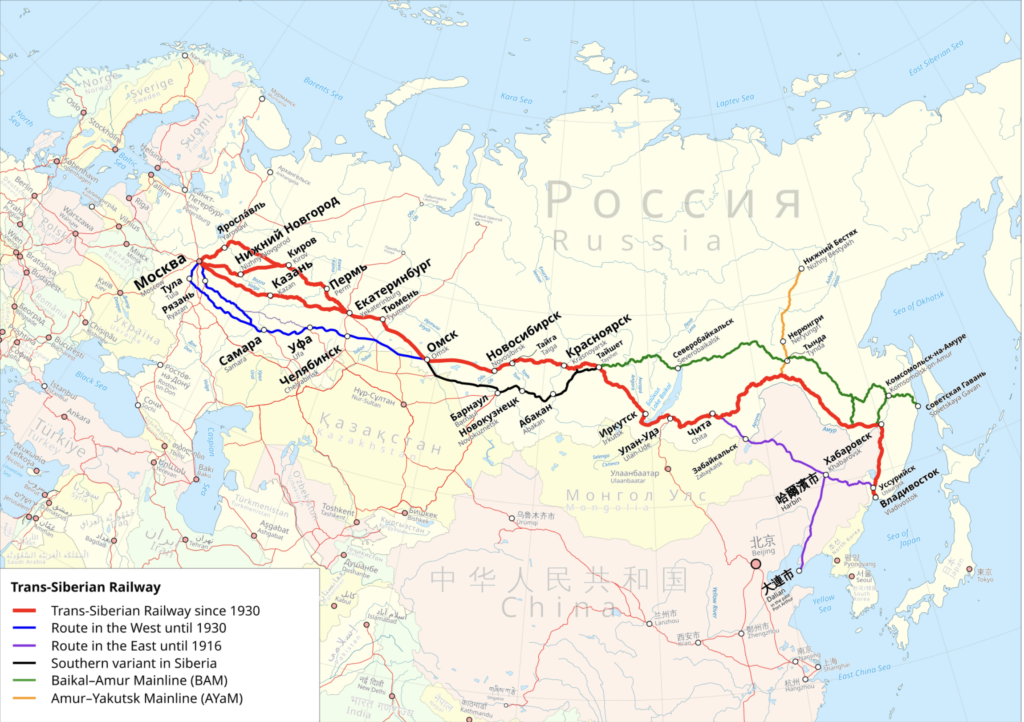
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over 9,289 kilometers (5,772 miles), it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the east.
During the period of the Russian Empire, government ministers —personally appointed by Alexander III and his son Nicholas II— supervised the building of the railway network between 1891 and 1916. Even before its completion, the line attracted travelers who documented their experiences. Since 1916, the Trans-Siberian Railway has directly connected Moscow with Vladivostok. As of 2021, expansion projects remain underway, with connections being built to Russia’s neighbors Mongolia, China, and North Korea. Additionally, there have been proposals and talks to expand the network to Tokyo, Japan, with new bridges or tunnels that would connect the mainland railway via the Russian island of Sakhalin and the Japanese island of Hokkaido.
The railway is often associated with the main transcontinental Russian line that connects many large and small cities of the European and Asian parts of Russia. At a Moscow–Vladivostok track length of 9.289 kilometers, it spans a record eight time zones. Taking eight days to complete the journey, it was the third-longest single continuous service in the world, after the Moscow–Pyongyang service 10.267 kilometers and the former Kiev–Vladivostok service 11.085 kilometers, both of which also follow the Trans-Siberian for much of their routes.
The main route begins in Moscow at Yaroslavsky Vokzal, runs through Yaroslavl or Chelyabinsk, Omsk, Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, Irkutsk, Ulan-Ude, Chita, and Khabarovsk to Vladivostok via southern Siberia. A second primary route is the Trans-Manchurian, which coincides with the Trans-Siberian east of Chita as far as Tarskaya (a stop 12 km east of Karymskoye, in Chita Oblast), about 1.000 km east of Lake Baikal. From Tarskaya the Trans-Manchurian heads southeast, via Harbin Harbin–Manzhouli railway and Mudanjiang Harbin–Suifenhe railway in China’s Northeastern provinces (from where a connection to Beijing is used by one of the Moscow–Beijing trains), joining the main route in Ussuriysk just north of Vladivostok.
The third primary route is the Trans-Mongolian Railway, which coincides with the Trans-Siberian as far as Ulan-Ude on Lake Baikal’s eastern shore. From Ulan-Ude the Trans-Mongolian heads south to Ulaanbaatar before making its way southeast to Beijing. In 1991, a fourth route running further to the north was finally completed, after more than five decades of sporadic work. Known as the Baikal–Amur Mainline (BAM), this recent extension departs from the Trans-Siberian line at Taishet several hundred miles west of Lake Baikal and passes the lake at its northernmost extremity. It crosses the Amur River at Komsomolsk-na-Amure (north of Khabarovsk), and reaches the Tatar Strait at Sovetskaya Gavan.